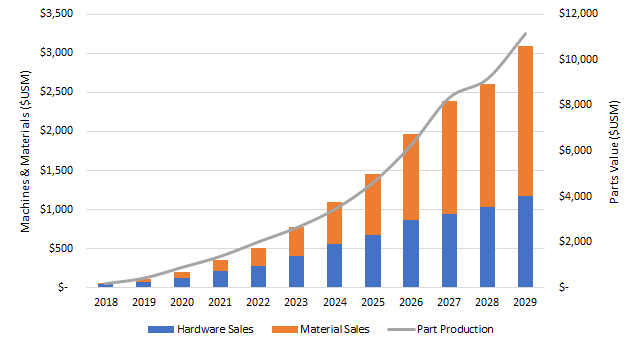
In SmarTech Publishing’s latest ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING WITH METAL POWDERS 2016: AN OPPORTUNITY ANALYSIS AND TEN-YEAR FORECAST report, we predict that the use of nickel alloys will grow at a faster pace than titanium, cobalt chrome, and stainless steel for the next five years. This is primarily due to to a wealth of recent applications stemming from use in aerospace, energy, and even medical applications using the popular super alloys Inconel, which are currently available for additive manufacturing in 718, 625, and 939 formulations.
New Nickel Alloy Applications in AM
SmarTech Publishing has identified several factors that suggest increased nickel alloys adoption across a variety of manufacturing segments
# 1. Increased adoption by aerospace sector expected. The aerospace industry is utilizing AM processes with nickel alloys in a number of high-value areas. These span the entirety of the aerospace industry, from commercial craft, to military, and even into space. Inconel has been the alloy of choice for various printed combustion chamber elements in space launch vehicles tested by NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, Space-X, and more.
# 2. New specialty surgical tools using Inconel. Surgical tools have recently been 3D printed in Inconel representing an interesting expansion of application for nickel alloys in AM. DanaMed created its Pathfinder ACL Guide that has been called a game changer for ACL surgical repair, and has significantly increased success rates associated with the procedure while reducing the incidence of re-tear.
# 3. Adoption by Arcam for EBM, production by AP&C. The only manufacturer of electron beam melting AM systems, Arcam (just acquired by GE), has recently introduced support for nickel alloys in its systems. AP&C, a subsidiary of Arcam, already produces nickel alloys utilizing its plasma atomization technology. Although the company focuses a significant amount of production on titanium alloys, its nickel alloy output has increased in recent years. Meanwhile, almost every major provider of metal powders utilizing gas atomization is now also providing nickel alloys for additive manufacturing.
# 4. Highest revenue generating alloy in automotive. Nickel is expected to become the most used alloy for AM in the automotive sector, growing alongside and often surpassing stainless steel to reach 452 tons used yearly in 2025 (vs 443 tons for stainless steel). At the same time it is expected to remain significantly more costly per kilogram than stainless steels, thus generating significantly more revenues than any other metal powder used in the automotive sector.
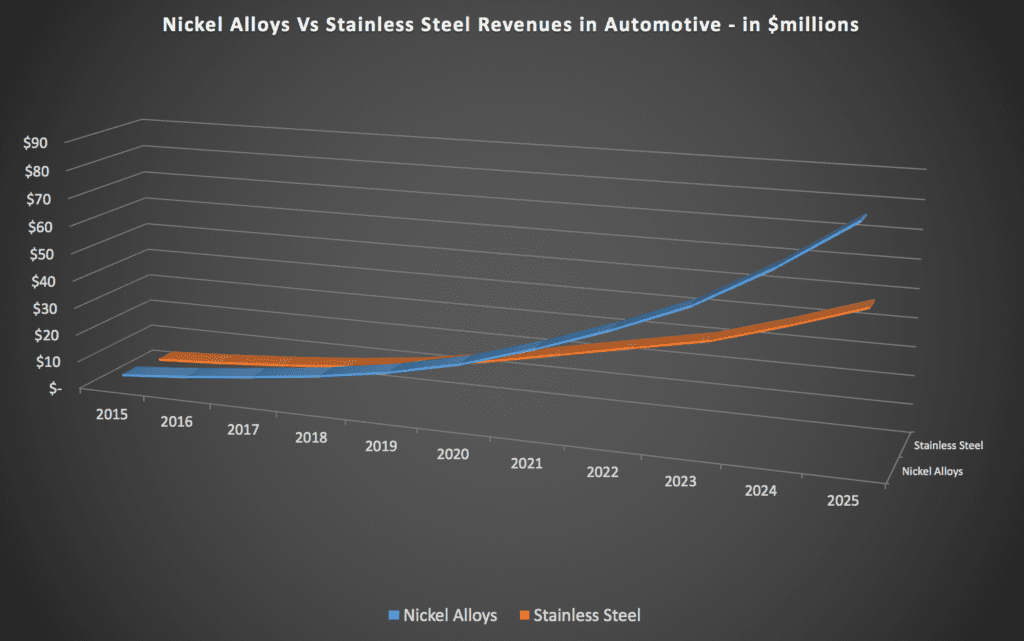
Revenues generated by nickel alloys in AM processes within the automotive sector are expected to remain higher than those generated by stainless steel, which is the other most used metal material in automotive.
Nickel Superalloys Will Shape the Future of AM
Nickel superalloys are utilized with all metal AM printing technologies (including binder jetting, electron beam powder bed fusion, and most commonly laser-based powder bed fusion and powder directed energy deposition): Nickel alloys are some of the most widely used metal powders in additive manufacturing today for a variety of high performance components, in both the area of functioning prototypes and true end-use components.
Today, the most popular by far are the Inconel superalloys, which are an exclusive trademark of the Special Metals Group and are currently available for additive manufacturing primarily in 718, 625 (and the less common) 939 formulations. Additional nickel alloys capable of being printed today include Hastalloy-X, a nickel-chromium-iron-molybdenum alloy that offers oxidation and high temperature resistance, high manufacturability and high resistance to stress-corrosion cracking in petrochemical applications.
These characteristics are also present in the more popular Inconel 718 and Iconel 625 powders for AM. These are also a high-strength, corrosion-resistant nickel chromium alloys (with the addition of molybdenum in 625).
Inconel 718 is known to retain its properties at temperatures ranging from -423°F to 1300°F. The ease and economy with which it can be fabricated (one Kg of powder costs about $200), combined with good tensile, fatigue, creep, and rupture strength, have resulted in its use in a wide range of applications. Inconel 625 is used for high strength, excellent manufacturability and corrosion resistance. Service temperatures range from cryogenic to 1800°F (982°C).
Possible applications for these nickel alloys span nearly the entire spectrum of additive manufacturing, from toolmaking to high functionality test parts, to one hundred percent end-use parts in critical applications — especially aerospace and defense markets. This is because Nickel alloys are highly valued for their significant heat resistant and corrosion resistant properties, along with good mechanical characteristics in tensile strength and endurance. For modern aircraft engines, roughly 50 percent of weight is typically from nickel alloy parts, making these alloys that much easier to transition to from an industry acceptance perspective.
About the Report:
SmarTech Publishing believes that these – combined with other elements relative to the general market for materials which are explored in Additive Manufacturing with Metal Powders 2016: An Opportunity Analysis and Ten-Year Forecast – will contribute to nickel’s establishment as one of the primary materials for AM and thus offer a significant opportunity to explore for the near to medium term future.
This report is the most comprehensive market study of metal additive manufacturing ever created, including analysis of
- Opportunities for metal powder suppliers
- The evolution of metal powder supply chains to meet the needs of evolving additive manufacturing markets
- Existing and emerging metal additive manufacturing technologies
- Metal-oriented 3D printing services
- End user industries and applications that are adopting metal printing
In this report, SmarTech Publishing presents a complete analysis of the powder manufacturing supply chain. No other source provides such a wealth of analysis and market data on metal additive manufacturing.
SmarTech Publishing’s industry-standard ten-year forecasts are applied in this report across the entire metal additive manufacturing sector – from print technology and install bases, to powder demand by adopting industry, to revenues associated with metal additive manufacturing materials.
If interested in receiving a quote or purchasing this report, please email missy@smartechpublishing.com.
Please also see our report 3D-Printed Metals: A Patent Landscape Analysis – 2016.
About SmarTech Publishing
SmarTech Publishing has published reports on most of the important revenue opportunities in the 3D printing sector including personal printers, low-volume manufacturing, 3D printing materials, medical/dental applications, aerospace and other promising 3D market segments. Our client roster includes some of the largest 3D printer firms, materials firms and investors in the world.
Since 2014, SmarTech Publishing has published dedicated, in-depth market studies focused on additive manufacturing opportunities in the metals sector.
Contact:
Lawrence Gasman
lawrence@smartechpublishing.com
434-872-0450